NGINX Management Suite Resiliency
The F5 NGINX Management Suite platform includes four services (described below) that work together to monitor NGINX data plane instances. These platform services feature self-monitoring capabilities, allowing them to detect unresolvable issues and shut down automatically. When you install NGINX Management Suite on Kubernetes, you get the benefits of fault tolerance and automated recovery: when a platform service fails, Kubernetes will create new pods and restart the affected services without disruption to the data plane.
Resilience refers to a system’s ability to bounce back from failures or disruptions through fault tolerance and automated recovery. High-availability, on the other hand, refers to a system’s ability to sustain uninterrupted operation despite any failures by means of redundancy, failover, and replication.
As the control plane for NGINX Open Source and NGINX Plus instances, the NGINX Management Suite is designed for resilience. Although NGINX Management Suite does not provide the same high-availability guarantees as the data plane, it is capable of quickly recovering from problems if they arise.
NGINX Management Suite includes the following four platform services that work together to monitor and manage NGINX data plane instances through APIs and web dashboards. When you install NGINX Management Suite on Kubernetes, these platform services are deployed as Kubernetes Deployments and are monitored by the Kubernetes control plane to ensure consistent and reliable operation.
Service |
Description |
|---|---|
| Core | The core service configures and sets up the management plane, as well as performs data analysis for metrics, events, and alerts. |
| Data Plane Manager (DPM) | The data plane manager (DPM) service is responsible for configuring NGINX instances on the data plane, monitoring the state of data plane resources, and generating reports and event messages. |
| Ingestion | The ingestion service collects metrics, security violations, and events that are not sent to the data plane manager service by the NGINX Agent. This information can be forwarded to external data stores. |
| Integrations | The integrations process includes features for interacting with external components, like configuring NGINX App Protect WAF policies, managing threat campaigns, and more. |
NGINX Management Suite uses Dqlite and ClickHouse databases, along with NATS streaming, for process coordination and event propagation. Each of these components requires persistent data storage to operate effectively.
The Core, DPM, and Integration platform services include an embedded Dqlite database. When NGINX Management Suite is deployed on Kubernetes, Kubernetes Persistent Volumes (PVs) are used for pods running the platform services. If a service needs to be restarted, the state and data of its Dqlite database can be restored.
NGINX Management Suite also uses a ClickHouse database, which can be installed from the Helm chart as a pod in the NGINX Management Suite namespace, or managed separately as a standalone cluster.
It’s also possible to run ClickHouse as a pod alongside the NGINX Management Suite pods, using a persistent volume for storage. Additionally, if preferred, NGINX Management Suite can be configured to connect to an externally-managed ClickHouse cluster hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS). This allows you to take advantage of custom high-availability architectures to meet your specific needs.
The following diagram shows the architecture of NGINX Management Suite deployed on Kubernetes.
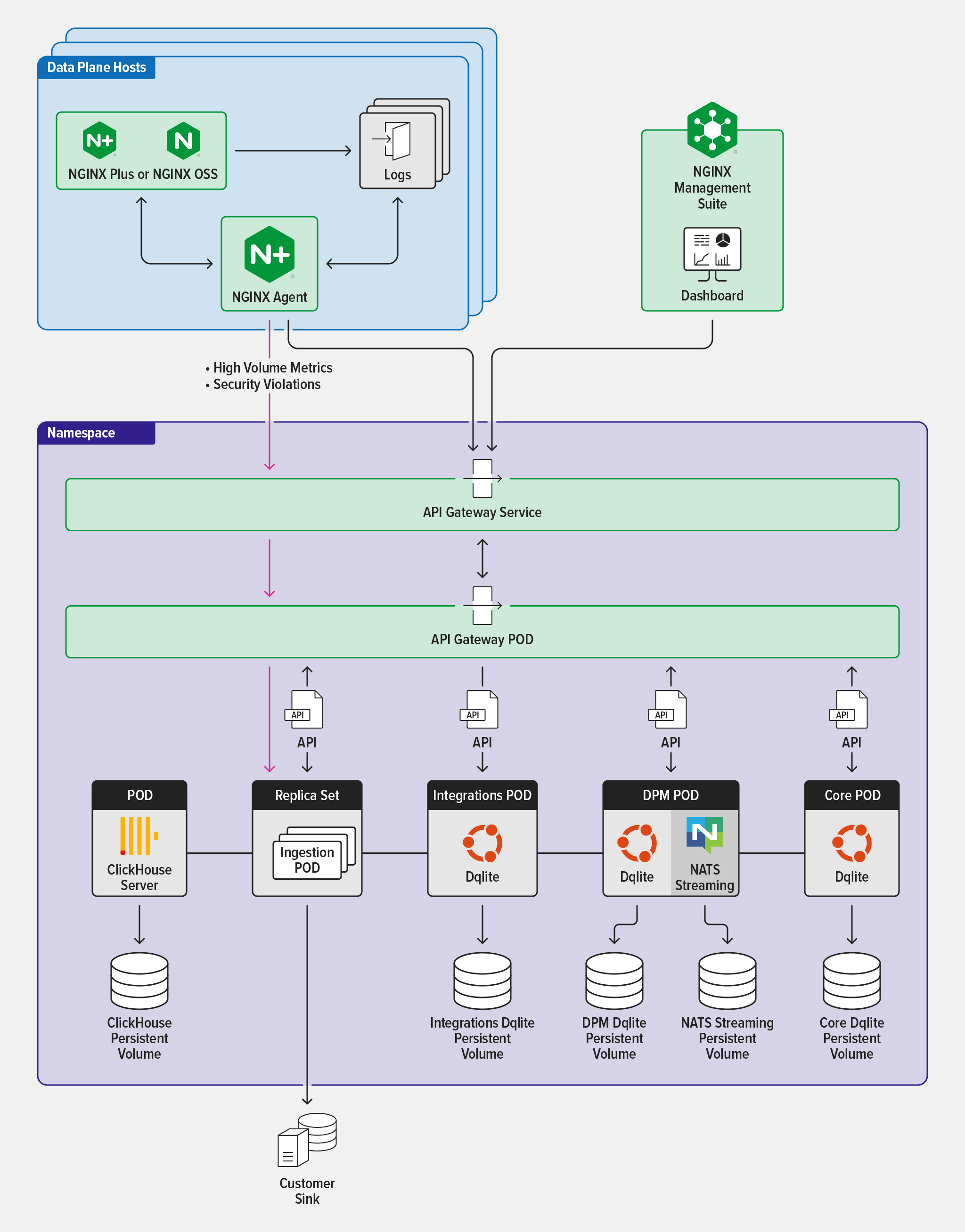
Figure 1. NGINX Management Suite Kubernetes deployment
If an NGINX Management Suite platform service fails or the node hosting the pod becomes unhealthy, Kubernetes will reschedule the pod to run on another node. The Kubernetes scheduler is subject to resource availability and node health in the cluster but will match pods to nodes as close to immediately as possible.
In an environment with the following specifications, we observed the following recovery times:
-
AWS EC2 Kubernetes v1.24 cluster
-
4 worker nodes (t3a.medium instances)
-
Low scheduler contention
-
Low CPU and memory pressure
-
Zero NGINX data plane proxies managed by NGINX Management Suite
-
NGINX Management Suite 2.9.0
-
ClickHouse pod as defined in the NGINX Management Suite helm chart
The time it took for the Pod condition
to transition from PodScheduled to Ready:
| Pod | Transition from PodScheduled to Ready |
|---|---|
| apigw | 2.2 seconds |
| core | 3.1 seconds |
| dpm | 3.95 seconds |
| integrations | 2.2 seconds |
| ingestion | 1.6 seconds |
| clickhouse | 17.75 seconds |
The recovery time for the DPM (Data Plane Manager) pod depends the number of NGINX data plane instances managed by NGINX Management Suite.
| Managed data plane instances | Average DPM recovery time |
|---|---|
| 0 managed instances | 3.95 seconds |
| 250 managed instances | 4.1 seconds |
| 500 managed instances | 5.45 seconds |
ImportantWhen integrating NGINX Management Suite into your existing Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BC/DR) strategy, consider the following:
NGINX data plane instances managed by NGINX Management Suite can serve traffic independently of the NGINX Management Suite control plane. Data plane instances will continue to operate seamlessly with their last published configurations as long as they remain healthy.
Use the replication or snapshot capabilities provided by your hosting solution to back up the persistent volumes used by NGINX Management Suite. Ensure that your organization’s backup and restore plan includes regular backups of NGINX Management Suite configuration files, Dqlite, and ClickHouse databases.
Establish specific metrics for your disaster recovery plan, such as Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO), for the NGINX Management Suite control plane independently of the data plane. Regularly review and update these metrics to consider the impact of data plane size on NGINX Management Suite services and storage requirements.
For resilient deployments, we recommend installing NGINX Management Suite on Kubernetes. With Kubernetes, you’ll get the benefits of persistent volumes and automated recovery for a reliable control plane.