Routing traffic to applications
Learn how to route external traffic to your Kubernetes applications using NGINX Gateway Fabric.
You can route traffic to your Kubernetes applications using the Gateway API and NGINX Gateway Fabric. Whether you’re managing a web application or a REST backend API, you can use NGINX Gateway Fabric to expose your application outside the cluster.
-
Install NGINX Gateway Fabric.
-
Save the public IP address and port of NGINX Gateway Fabric into shell variables:
GW_IP=XXX.YYY.ZZZ.III GW_PORT=<port number>
The application we are going to use in this guide is a simple coffee application comprised of one service and two pods:
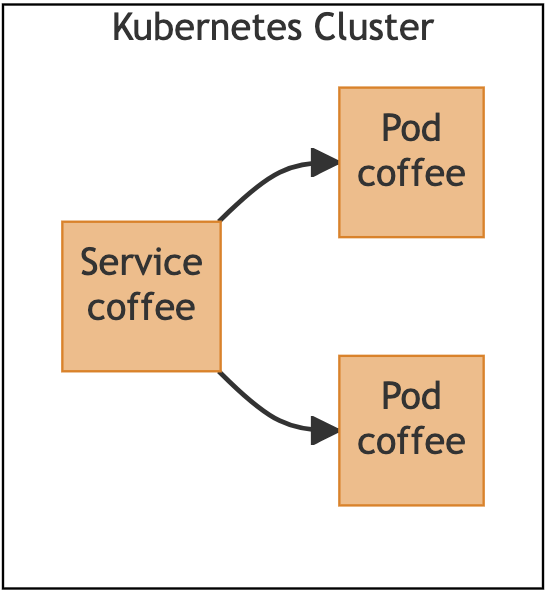
Using this architecture, the coffee application is not accessible outside the cluster. We want to expose this application on the hostname “cafe.example.com” so that clients outside the cluster can access it.
Install NGINX Gateway Fabric and create two Gateway API resources: a gateway and an HTTPRoute.
Using these resources we will configure a simple routing rule to match all HTTP traffic with the hostname “cafe.example.com” and route it to the coffee service.
Create the coffee application in Kubernetes by copying and pasting the following block into your terminal:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: coffee
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: coffee
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: coffee
spec:
containers:
- name: coffee
image: nginxdemos/nginx-hello:plain-text
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: coffee
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app: coffee
EOFThis will create the coffee service and a deployment with two pods. Run the following command to verify the resources were created:
kubectl get pods,svcYour output should include two coffee pods and the coffee service:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/coffee-7dd75bc79b-cqvb7 1/1 Running 0 77s
pod/coffee-7dd75bc79b-dett3 1/1 Running 0 77s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/coffee ClusterIP 198.51.100.1 <none> 80/TCP 77sTo route traffic to the coffee application, we will create a gateway and HTTPRoute. The following diagram shows the configuration we are creating in the next step:
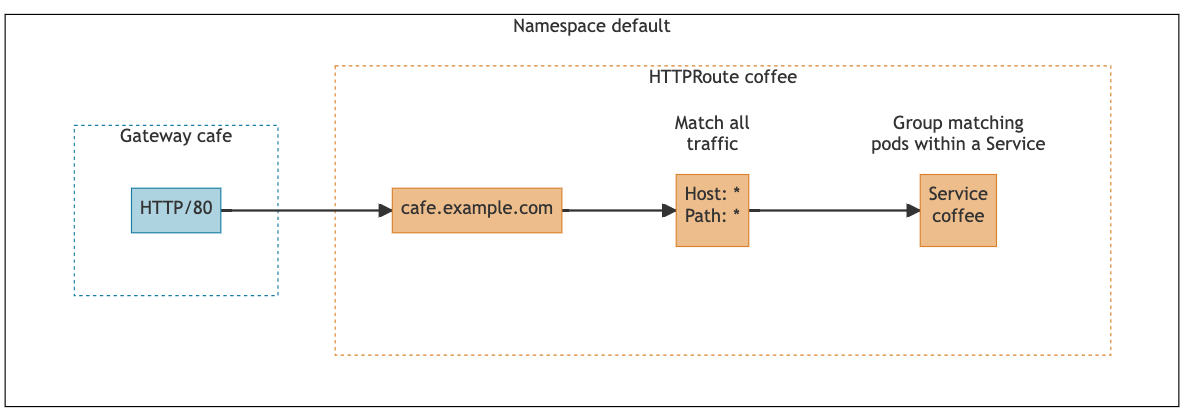
We need a gateway to create an entry point for HTTP traffic coming into the cluster. The cafe gateway we are going to create will open an entry point to the cluster on port 80 for HTTP traffic.
To route HTTP traffic from the gateway to the coffee service, we need to create an HTTPRoute named coffee and attach it to the gateway. This HTTPRoute will have a single routing rule that routes all traffic to the hostname “cafe.example.com” from the gateway to the coffee service.
Once NGINX Gateway Fabric processes the cafe gateway and coffee HTTPRoute, it will configure its data plane (NGINX) to route all HTTP requests sent to “cafe.example.com” to the pods that the coffee service targets:
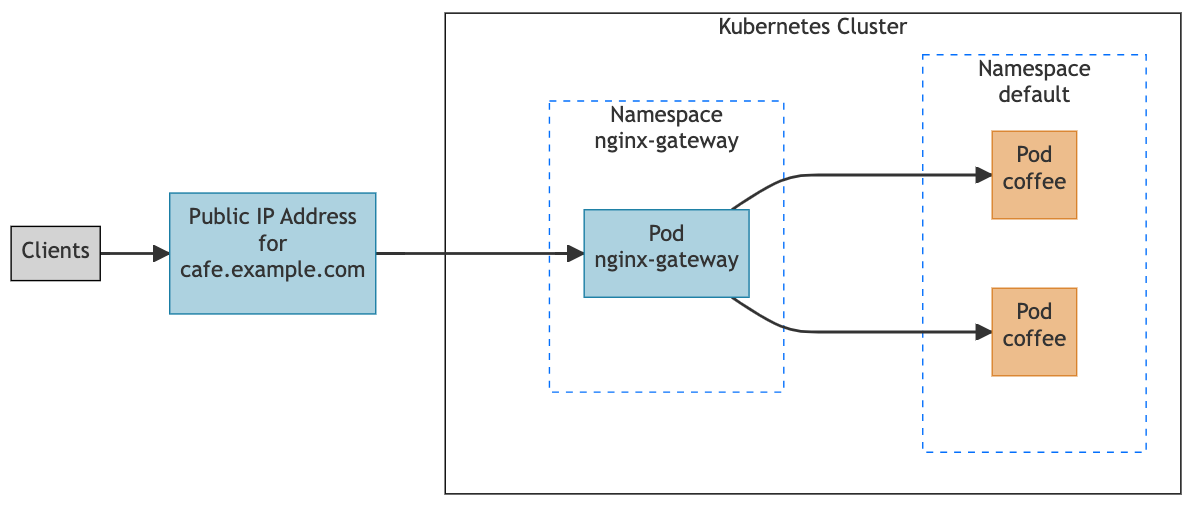
The coffee service is omitted from the diagram above because the NGINX Gateway Fabric routes directly to the pods that the coffee service targets.
Note:In the diagrams above, all resources that are the responsibility of the cluster operator are shown in blue. The orange resources are the responsibility of the application developers.
See the roles and personas Gateway API document for more information on these roles.
To create the cafe gateway, copy and paste the following into your terminal:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: cafe
spec:
gatewayClassName: nginx
listeners:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: HTTP
EOFThis gateway is associated with the NGINX Gateway Fabric through the gatewayClassName field. The default installation of NGINX Gateway Fabric creates a GatewayClass with the name nginx. NGINX Gateway Fabric will only configure gateways with a gatewayClassName of nginx unless you change the name via the --gatewayclass command-line flag.
We specify a listener on the gateway to open an entry point on the cluster. In this case, since the coffee application accepts HTTP requests, we create an HTTP listener, named http, that listens on port 80.
By default, gateways only allow routes (such as HTTPRoutes) to attach if they are in the same namespace as the gateway. If you want to change this behavior, you can set the allowedRoutes field.
Next you will create the HTTPRoute by copying and pasting the following into your terminal:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: coffee
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: cafe
hostnames:
- "cafe.example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: coffee
port: 80
EOFTo attach the coffee HTTPRoute to the cafe gateway, we specify the gateway name in the parentRefs field. The attachment will succeed if the hostnames and protocol in the HTTPRoute are allowed by at least one of the gateway’s listeners.
The hostnames field allows you to list the hostnames that the HTTPRoute matches. In this case, incoming requests handled by the http listener with the HTTP host header “cafe.example.com” will match this HTTPRoute and will be routed according to the rules in the spec.
The rules field defines routing rules for the HTTPRoute. A rule is selected if the request satisfies one of the rule’s matches. To forward traffic for all paths to the coffee service we specify a match with the PathPrefix “/” and target the coffee service using the backendRef field.
To test the configuration, we will send a request to the public IP and port of NGINX Gateway Fabric that you saved in the Before you begin section and verify that the response comes from one of the coffee pods.
Note: Your clients should be able to resolve the domain name “cafe.example.com” to the public IP of the NGINX Gateway Fabric. In this guide we will simulate that using curl’s--resolveoption.
First, let’s send a request to the path “/”:
curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/We should get a response from one of the coffee pods:
Server address: 10.12.0.18:8080
Server name: coffee-7dd75bc79b-cqvb7Since the cafe HTTPRoute routes all traffic on any path to the coffee application, the following requests should also be handled by the coffee pods:
curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/some-pathServer address: 10.12.0.18:8080
Server name: coffee-7dd75bc79b-cqvb7curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/some/pathServer address: 10.12.0.19:8080
Server name: coffee-7dd75bc79b-dett3Requests to hostnames other than “cafe.example.com” should not be routed to the coffee application, since the cafe HTTPRoute only matches requests with the “cafe.example.com"need hostname. To verify this, send a request to the hostname “pub.example.com”:
curl --resolve pub.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://pub.example.com:$GW_PORT/You should receive a 404 Not Found error:
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.25.2</center>
</body>
</html>If you have any issues while testing the configuration, try the following to debug your configuration and setup:
-
Make sure you set the shell variables $GW_IP and $GW_PORT to the public IP and port of the NGINX Gateway Fabric Service. Refer to the Installation guides for more information.
-
Check the status of the gateway:
kubectl describe gateway cafeThe gateway status should look similar to this:
Status: Addresses: Type: IPAddress Value: 10.244.0.85 Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Gateway is accepted Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Accepted Status: True Type: Accepted Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Gateway is programmed Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Programmed Status: True Type: Programmed Listeners: Attached Routes: 1 Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Listener is accepted Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Accepted Status: True Type: Accepted Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Listener is programmed Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Programmed Status: True Type: Programmed Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: All references are resolved Observed Generation: 1 Reason: ResolvedRefs Status: True Type: ResolvedRefs Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: No conflicts Observed Generation: 1 Reason: NoConflicts Status: False Type: Conflicted Name: httpCheck that the conditions match and that the attached routes for the http listener equals 1. If it is 0, there may be an issue with the HTTPRoute.
-
Check the status of the HTTPRoute:
kubectl describe httproute coffeeThe HTTPRoute status should look similar to this:
Status: Parents: Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: The route is accepted Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Accepted Status: True Type: Accepted Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: All references are resolved Observed Generation: 1 Reason: ResolvedRefs Status: True Type: ResolvedRefs Controller Name: gateway.nginx.org/nginx-gateway-controller Parent Ref: Group: gateway.networking.k8s.io Kind: Gateway Name: cafe Namespace: defaultCheck for any error messages in the conditions.
-
Check the generated nginx config:
kubectl exec -it -n nginx-gateway <nginx gateway pod> -c nginx -- nginx -TThe config should contain a server block with the server name “cafe.example.com” that listens on port 80. This server block should have a single location
/that proxy passes to the coffee upstream:server { listen 80; server_name cafe.example.com; location / { ... proxy_pass http://default_coffee_80$request_uri; # the upstream is named default_coffee_80 ... } }There should also be an upstream block with a name that matches the upstream in the proxy_pass directive. This upstream block should contain the pod IPs of the coffee pods:
upstream default_coffee_80 { ... server 10.12.0.18:8080; # these should be the pod IPs of the coffee pods server 10.12.0.19:8080; ... }
Note: The entire configuration is not shown because it is subject to change. Ellipses indicate that there’s configuration not shown.
If your issue persists, contact us.
To learn more about the Gateway API and the resources we created in this guide, check out the following resources: