Application routes using HTTP matching conditions
Learn how to deploy multiple applications and HTTPRoutes with request conditions such as paths, methods, headers, and query parameters
Overview
In this guide we will configure advanced routing rules for multiple applications. These rules will showcase request matching by path, headers, query parameters, and method. For an introduction to exposing your application, we recommend that you follow the basic guide first.
The following image shows the traffic flow that we will be creating with these rules.
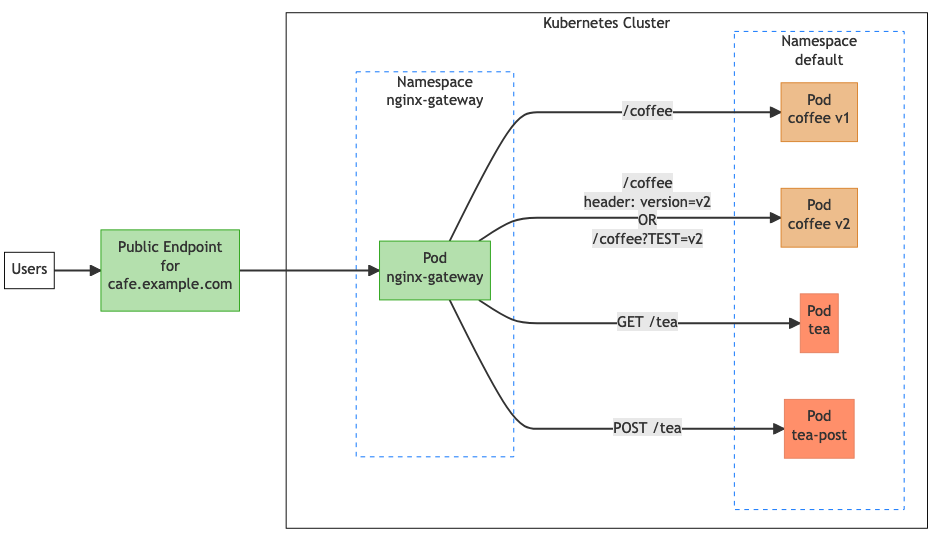
The goal is to create a set of rules that will result in client requests being sent to specific backends based on the request attributes. In this diagram, we have two versions of the coffee service. Traffic for v1 needs to be directed to the old application, while traffic for v2 needs to be directed towards the new application. We also have two tea services, one that handles GET operations and one that handles POST operations. Both the tea and coffee applications share the same Gateway.
Before you begin
-
Install NGINX Gateway Fabric.
-
Save the public IP address and port of NGINX Gateway Fabric into shell variables:
GW_IP=XXX.YYY.ZZZ.III GW_PORT=<port number>
Note:
In a production environment, you should have a DNS record for the external IP address that is exposed, and it should refer to the hostname that the gateway will forward for.
Coffee applications
Deploy the Coffee applications
Begin by deploying the coffee-v1 and coffee-v2 applications:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nginxinc/nginx-gateway-fabric/v1.4.0/examples/advanced-routing/coffee.yaml
Deploy the Gateway API Resources for the Coffee applications
The gateway resource is typically deployed by the cluster operator. To deploy the gateway:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: cafe
spec:
gatewayClassName: nginx
listeners:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: HTTP
EOF
This gateway defines a single listener on port 80. Since no hostname is specified, this listener matches on all hostnames.
The HTTPRoute is typically deployed by the application developer. To deploy the coffee HTTPRoute:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: coffee
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: cafe
sectionName: http
hostnames:
- cafe.example.com
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /coffee
backendRefs:
- name: coffee-v1-svc
port: 80
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /coffee
headers:
- name: version
value: v2
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /coffee
queryParams:
- name: TEST
value: v2
backendRefs:
- name: coffee-v2-svc
port: 80
EOF
This HTTPRoute has a few important properties:
-
The
parentRefsreferences the gateway resource that we created, and specifically defines thehttplistener to attach to, via thesectionNamefield. -
cafe.example.comis the hostname that is matched for all requests to the backends defined in this HTTPRoute. -
The first rule defines that all requests with the path prefix
/coffeeand no other matching conditions are sent to thecoffee-v1Service. -
The second rule defines two matching conditions. If either of these conditions match, requests are forwarded to the
coffee-v2Service:- Request with the path prefix
/coffeeand headerversion=v2 - Request with the path prefix
/coffeeand the query parameterTEST=v2
If you want both conditions to be required, you can define headers and queryParams in the same match object.
- Request with the path prefix
Send traffic to Coffee
Using the external IP address and port for NGINX Gateway Fabric, we can send traffic to our coffee applications.
Note:
If you have a DNS record allocated forcafe.example.com, you can send the request directly to that hostname, without needing to resolve.
curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/coffee
This request should receive a response from the coffee-v1 Pod.
Server address: 10.244.0.9:8080
Server name: coffee-v1-76c7c85bbd-cf8nz
If we want our request to be routed to coffee-v2, then we need to meet the defined conditions. We can include a header:
curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/coffee -H "version:v2"
or include a query parameter:
curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/coffee?TEST=v2
Either request should result in a response from the coffee-v2 Pod.
Server address: 10.244.0.9:8080
Server name: coffee-v2-68bd55f798-s9z5q
Tea applications
Let’s deploy a different set of applications now called tea and tea-post. These applications will have their own set of rules, but will still attach to the same gateway listener as the coffee apps.
Deploy the Tea applications
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nginxinc/nginx-gateway-fabric/v1.4.0/examples/advanced-routing/tea.yaml
Deploy the HTTPRoute for the Tea services
We are reusing the previous gateway for these applications, so all we need to create is the HTTPRoute.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: tea
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: cafe
hostnames:
- cafe.example.com
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /tea
method: POST
backendRefs:
- name: tea-post-svc
port: 80
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /tea
method: GET
backendRefs:
- name: tea-svc
port: 80
EOF
The properties of this HTTPRoute include:
- The same gateway is referenced as before.
- The same hostname is used as with the
coffeeapps. - The first rule defines that a POST request to the
/teapath is routed to thetea-postService. - The second rule defines that a GET request to the
/teapath is routed to theteaService.
Send traffic to Tea
Using the external IP address and port for NGINX Gateway Fabric, we can send traffic to our tea applications.
Note:
If you have a DNS record allocated forcafe.example.com, you can send the request directly to that hostname, without needing to resolve.
curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/tea
This GET request should receive a response from the tea Pod.
Server address: 10.244.0.10:8080
Server name: tea-df5655878-5fmfg
If we want our request to be routed to tea-post, then we need to send a POST request:
curl --resolve cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT:$GW_IP http://cafe.example.com:$GW_PORT/tea -X POST
Server address: 10.244.0.7:8080
Server name: tea-post-b59b8596b-g586r
This request should receive a response from the tea-post pod. Any other type of method, such as PATCH, will result in a 404 Not Found response.
Troubleshooting
If you have any issues while sending traffic, try the following to debug your configuration and setup:
-
Make sure you set the shell variables $GW_IP and $GW_PORT to the public IP and port of the NGINX Gateway Fabric service. Refer to the Installation guides for more information.
-
Check the status of the Gateway:
kubectl describe gateway cafeThe Gateway status should look like this:
Status: Addresses: Type: IPAddress Value: 10.244.0.85 Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Gateway is accepted Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Accepted Status: True Type: Accepted Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Gateway is programmed Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Programmed Status: True Type: Programmed Listeners: Attached Routes: 2 Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Listener is accepted Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Accepted Status: True Type: Accepted Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: Listener is programmed Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Programmed Status: True Type: Programmed Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: All references are resolved Observed Generation: 1 Reason: ResolvedRefs Status: True Type: ResolvedRefs Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: No conflicts Observed Generation: 1 Reason: NoConflicts Status: False Type: Conflicted Name: httpCheck that the conditions match and that the attached routes for the
httplistener equals 2. If it is less than 2, there may be an issue with the routes. -
Check the status of the HTTPRoutes:
kubectl describe httproute coffeekubectl describe httproute teaEach HTTPRoute status should look like this:
Status: Parents: Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: The route is accepted Observed Generation: 1 Reason: Accepted Status: True Type: Accepted Last Transition Time: 2023-08-15T20:57:21Z Message: All references are resolved Observed Generation: 1 Reason: ResolvedRefs Status: True Type: ResolvedRefs Controller Name: gateway.nginx.org/nginx-gateway-controller Parent Ref: Group: gateway.networking.k8s.io Kind: Gateway Name: cafe Namespace: defaultCheck for any error messages in the conditions.
Further reading
To learn more about the Gateway API and the resources we created in this guide, check out the following Kubernetes documentation resources: